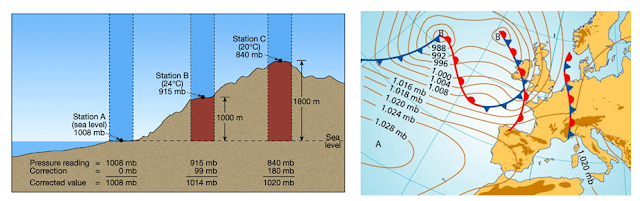
Difference Between Absolute and Gauge Pressure

Pressure can be described as the force applied to an area. There are many different systems of pressure measurement, with absolute pressure and sealed gauge pressure being two of the most common. There are many differences between these two measurements of pressure that have significant effects on their use and measurement. Depending on why you are measuring pressure, determining whether you need gauge or absolute reference pressure is as important as selecting the pressure range itself, particularly for low pressure. If you get it wrong it could create huge errors in your measurements. The simplest way to explain the difference between the two is that absolute pressure uses absolute zero as its zero point, while gauge pressure uses atmospheric pressure as its zero point. Due to varying atmospheric pressure, gauge pressure measurement is not precise, while absolute pressure is always definite. Gauge Pressure The most common pressure reference is gauge pressure which is signified by