SỰ KHÁC NHAU GIỮA ÁP SUẤT TUYỆT ĐỐI, TƯƠNG ĐỐI VÀ CHÊNH ÁP
Bất kỳ một kỹ thuật viên đo lường nào cũng cần phải biết sự khác nhau giữa các loại đo áp suất cơ bản.
Vậy áp suất là gì?
Áp suất khí quyển - định nghĩa
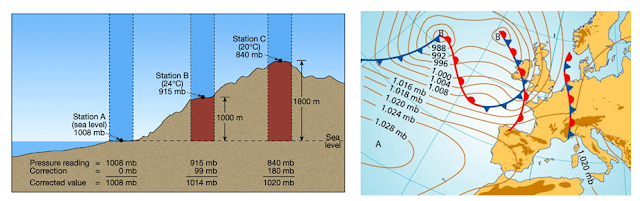
It is caused by the weight of the atmosphere. It depends on the climatic changes, the reference pressure is the pressure at sea level which is equal to 1013 mbar or 760 mmHg.
It can have a variation of ± 200 mbar depending on the height above the sea level, and variation of ± 30 mbar per day depending on weather conditions.
Vậy áp suất là gì?
Áp suất khí quyển - định nghĩa
It is caused by the weight of the atmosphere. It depends on the climatic changes, the reference pressure is the pressure at sea level which is equal to 1013 mbar or 760 mmHg.
It can have a variation of ± 200 mbar depending on the height above the sea level, and variation of ± 30 mbar per day depending on weather conditions.
Absolute Pressure – Definition and applications
- It is defined as the pressure referred to absolute zero pressure.
- Always take into account the atmospheric pressure
- It can be recognized by the subscript abs. Another way to define it is add to the atmospheric pressure the value of pressure gauge taken from the instrumentation.
Absolute Pressure – Definition and applications
- It is defined as the pressure referred to absolute zero pressure.
- Always take into account the atmospheric pressure
- It can be recognized by the subscript abs. Another way to define it is add to the atmospheric pressure the value of pressure gauge taken from the instrumentation.
Applications:
- Applications where high accuracy of vacuum measurement is required.
- Control applications where low pressure or vacuum is needed. In these applications it is necessary to have a measure that takes into account the influence of atmospheric pressure.
- Measurement of low pressure in the distillation vacuum columns.
- Vacuum Reactors
- Leakage control in tanks and circuits
Gauge Pressure – Definition and applications
- It depends on an element that measures the difference between absolute pressure and atmospheric.
- Does not take into account the effect of atmospheric pressure
- It can be recognized by the subscript reg or g (gauge).
- They constitute 95% of the types of meters installed in the chemical industry.
- It can be positive (P1> Patm) or negative also known as vacuum (P1 <Patm)
Applications:
- Measurement of level in atmospheric tanks
- Measurement of Pressure in pipes and tanks where working pressure is greater than the variations due to atmospheric pressure. The change in atmospheric pressure have no impact in the final pressure measurement.
- Measurement of pressure in air conditioning and air control and corrosive gases. For example in lab rooms.
Differential Pressure – Definition and applications
- nó được định nghĩa là sự chênh lệch giữa 2 áp suất. hay còn gọi là DP, It is defined as the difference between two pressures, also known as dP, loss, etc …
- It does not take into account the effect of atmospheric pressure
Applications:
- Level measurement in tanks and vessels
- Density measurement
- Flow Measurement
- Interface Level Measurement
- Flooding Monitoring in Distillation Column
- Filter monitoring
- Monitoring pumps and valves
- Fire Monitoring Systems – Sprinklers
- Processes where is needed a supply pressure monitoring
Pressure Measurement Facts
- Barometric pressure has influence in the measurement of the absolute pressure, its effect is inversely proportional to the measurement range of the equipment (Greater Range Effect to Low).
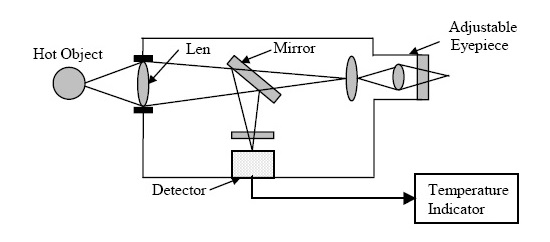
What instrument is used to measure air pressure?
- The Barometer is the instrument used to measure air pressure.
Summary








Comments
Post a Comment